I have often wondered about the purpose of a bond. How is a bond any different than having insurance? You get a bond through an insurance company, so what’s the difference? Why are businesses sometimes required to have both?
As it turns out, even though a bond is sold by an insurance agent, it is often not considered one of the many types of insurance. It has more parties involved, and pays claims differently than insurance policies.
Regardless, a bond can absolutely be considered a type of insurance
DEFINITION OF INSURANCE
The definition of insurance is an arrangement for compensation when damage occurs. Damage can be anything that has gone wrong. It does not have to be physical damage. It can be a setback or an impairment. It can even be financial harm.

An insurance policy is an agreement between two parties: the insured, known as the policy owner, and the insurer, known as the insurance company or insurance carrier. It’s a two-party contract. Sometimes a third party is compensated on behalf of the insured, like in a car accident, but they are not listed anywhere on the insurance policy.
HOW INSURANCE WORKS
When a claim is filed by the insured and paid by the insurance company, the insurance company does NOT expect to be reimbursed by the insured. Rates may increase, but a policy owner is not expected to repay a claim.
There are cases where an insurance company will expect to be reimbursed by another party that is responsible for damages, but never be repaid by the insured. Repayment of a claim by a 3rd party is referred to as subrogation.
Insurance carriers do not subrogate against their policy owner.
One of the major differences in a bond vs insurance is that a bond company will expect to be fully reimbursed by their customer, the purchase of the bond, known as the principal.

An insurance company pays claims for damages that setback the policy owner. Like a homeowners claim after a windstorm, or an auto accident regardless of who’s at fault, or when you get hurt on the job and you file a workers compensation claim.
Bonds don’t pay these types of claims. Bonds pay when you don’t hold true to your word or work.
DEFINITION OF A BOND
A bond is a form of assurance. The definition of assurance is to make certain that something happens.
Bonds are issued by insurance companies and sold by insurance agents. They are not general liability insurance nor are they professional liability insurance. They are not considered a form of insurance at all. However, my definition of insurance above states in a slightly different manner that a bond does indeed offer compensation when damage occurs.
Sometimes a bond is referred to as a form of credit. I do not agree with this. Maybe forms of security but not credit. Credit is borrowing against something, like a line of credit, and repaying it.
HOW A BOND WORKS
A bond is more of a backing or financial support. Bonds are forms of financial guarantee and financial security. They are not a line of credit.
In the event of a claim a bond must be repaid by the principal, but you do not borrow against a bond like you would with a line of credit.
Because bonds must be repaid if a claim is paid out, bonds are credit based. Meaning your credit history and credit scores are factored into determining the rate you pay for the bond. When your credit ratings is not where the bond company would like it to be, a higher rate is charged. And in some cases a bond is declined due to credit.
This is similar to how you obtain an insurance policy. Most policies are credit rated. You’re likely to get a better price on your home owners insurance when you have better credit.
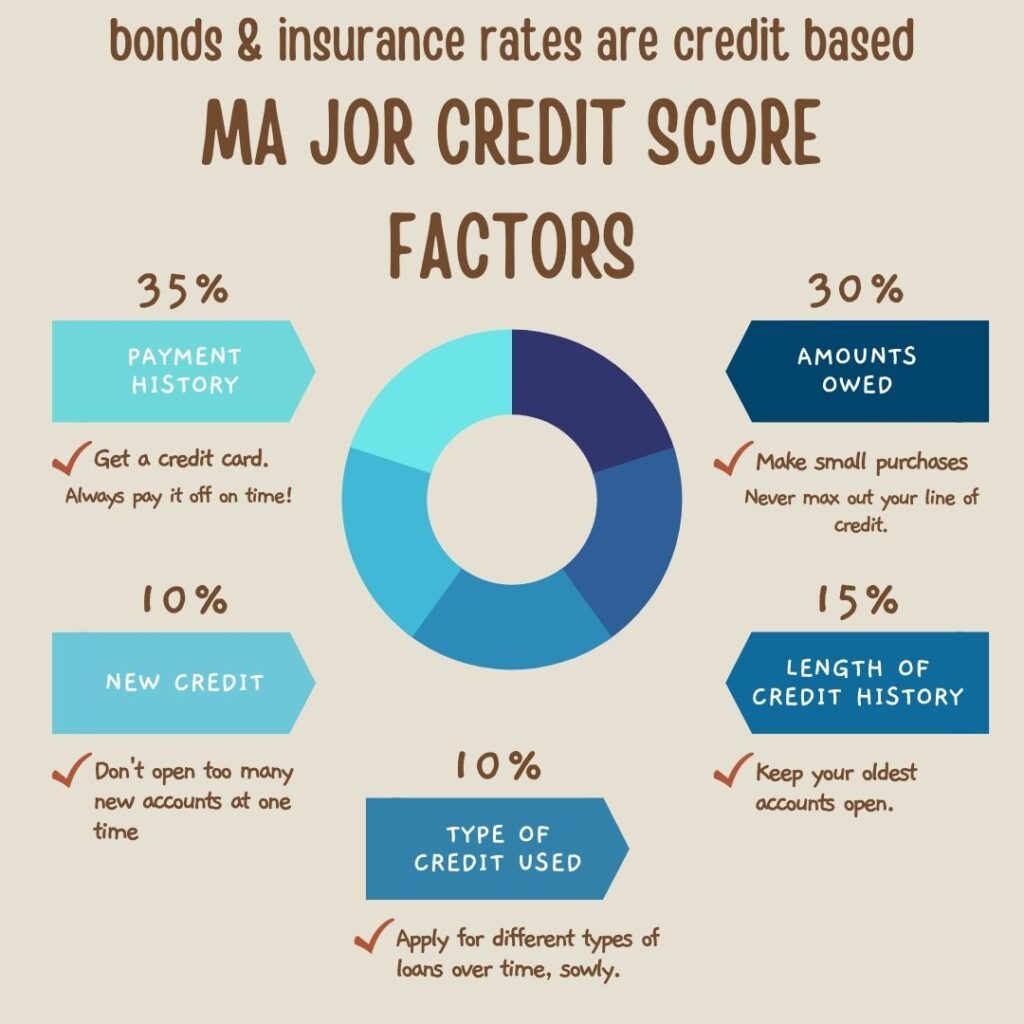
Insurance companies have performed extensive research that shows individuals with a higher credit score tend to have less risk of loss. Better credit equals less claims, less financial losses for the insurance carrier. The same study applies to bonds.
When a bond is issued, it supports the principal. The principal is essentially the policy owner, the person buying the bond. The support comes in the form of financially backing the principal’s ability to perform a task to uphold their contractual obligations.
The bond states that it will back the word and work of the principal. It goes on to state that in the event the principal does not hold true to his word and/or work, the bond will compensate the obligee for the bond amount. Now the bond is supporting the obligee.
The obligee is specifically listed on the bond as the person, municipality, or business that is compensated in the event of a claim against the principal. There is no obligee on an insurance policy.
Because a bond claim must be repaid, the bond company cares about your credit.
KEY DIFFERENCES AND SIMILARITIES
Both, a bond and an insurance policy, have a premium that is charged to have the protection offered. However, bonds tend to have less claims, therefore bond premiums are significantly less than your business insurance premium.
Just like with insurance policies, there are many types of bonds. The most common bond is a surety bond. A surety bond is required for any work being done for a municipality. Construction contracts with any government entity will always require a bond.
There are fidelity bonds, performance bonds, contractor bonds, license and permit bonds, auto dealer bonds, there are even payment bonds. There are just about as many bond types as there are types of insurance policies.

The bond company and the insurance company play the same role. The principal and the policy owner play the same role.
The main difference between a bond and an insurance policy is that of who is getting paid and why.
A bond has an obligee. The claim is paid to the obligee. An insurance policy has a policy owner. The insurance claim is most often paid to the policy owner, the insured.
A bond is your financial reference, much like a letter of credit. An insurance policy is your financial safety net.
As you can tell, bonds are a financial backing for a totally different type of damage than that of an insurance product. You can see how a bond could be considered a type of insurance policy, but then why most of the time it’s not.
